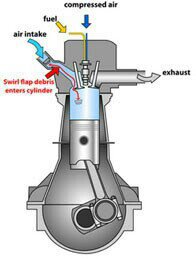
Swirl flaps are a BMW system that has been introduced to help burn the fuel mixture in the cylinder better due to the fact that diesel engines do not have throttle valves and it is not possible to adjust the air-fuel ratio. A diesel engine without vortex valves operates between a poor and a rich fuel mixture, because the only way to regulate it is through fuel injection.
Design of the first generation swirl flaps that are made of made of metal.

Unfortunately, swirl flaps are responsible for countless damaged engines and costly repairs due to design errors or metal fatigue. Once damaged, the cylinder sucks them in and causes great damage.
This is how damaged valves damage the cylinder.
Typical swirl flaps suction damage.

The vortex valves are positioned in the inlet and are controlled by vacuum (DDE 4.0) or electrically (DDE5.0 / DDE6.4) by the engine ECU.
Effects of malfunctioning valves:
- Swirl valves are stuck in open position: Deterioration of exhaust gas performance at lower speeds.
- Swirl valves are stuck in closed position: Approximate power loss of 10% at high engine speeds.
How swirl flaps work:
Performance characteristics:
The vortex valves are in the closed position, at low engine speeds and small amounts of fuel injected (controlled by the ECU card).
They open under the following conditions:
- coolant temperature <14 ° C OR * fuel quantity> 24 mg OR
2. engine speed 2250 rpm OR
3. inlet air temperature <-5 ° C.
BMW and Pierburg have decided to produce diesel engines with metal vortex valves. The speed at which the pistons in the diesel engine operate is at least 60 rpm, so a sucked vortex valve will break and cause a number of damages inside the engine.
In most cases, one or more pistons are severely damaged, as a bonus you get valves, in some cases a head or turbocharger. And this combination with a BMW engine is like a cumulative jackpot 🙂
In 2004, BMW began work on the problem and improved the design, however, a number of owners reported ongoing problems in this area.
The solution to this problem is by removing the vortex valves and plugging, which does not affect the performance of the engine and at the same time, you can safely pass the exhaust test.
Engines:
M47 (136hp VP44 fuel pump) has no valves.
M47N common rail engine (including M47N / M47TU / M47TUD20) (150hp. Face lift model from 2001 -) has valves.
M57 engines (M57D) (525d & 187hp. 330d) cars with manual transmission do not have valves, but those with automatic have.
M57N engines (M57TUD) (525d & 330d 204hp) have vortex valves.
Ruined swirl flapss:
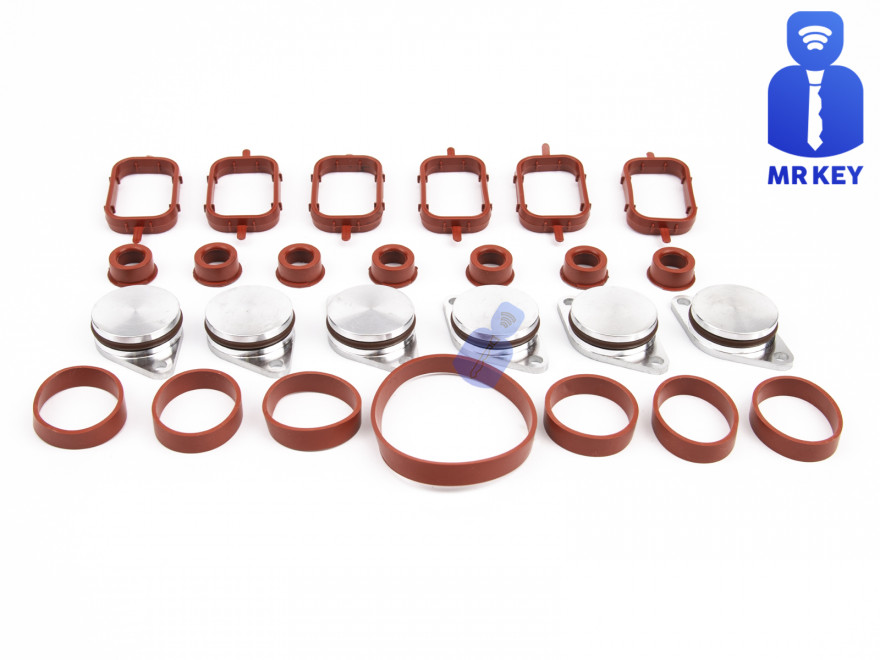
The plugs that replace the vortex valves are easy to find on the internet, but you can also find them here on our website.
Typical plugs:

Disassembly of vortex valves:
The vortex valves can be safely dismantled and in most cases if they are removed properly no loss of power is felt.
Final list of models for which vortex valves are installed:
Engine: M47N/M47TU/M47TUD20
Applications:
* 110 kW (148 hp) and 330 N·m (243 lb·ft)
o E46 320d 2001-2005
o E83 X3 2.0d (up to end of 2006)
Engine: M47TU2D20
The engine was updated again in 2004 as the M47TU2D20. Still at 1995 cc, it produced more power across the range.
Applications:
* 120 kW (161 hp) and 340 N·m (251 lb·ft)
E60/E61 520d
E87 120d
E90/E91 320d
E83 X3 2.0d (end of 2006 onwards)
Engine: M57/M57D25
M57D25 was introduced in 2000.
Applications:
* 166 PS (122 kW; 164 hp) at 4000 rpm, 350 N·m (260 lb·ft) at 2000-2500 rpm with a 4750 rpm redline, models:
2000-2003 E39 525d *Vehicles With Automatic Transmission ONLY*
Engine: M57N/M57TU/M57TUD25
M57TUD25 was introduced in 2004.
Applications:
* 177 PS (130 kW; 175 hp) at 4000 rpm, 400 N·m (300 lb·ft) at 2000-2750 rpm models:
E60/E61 525d
Engine: M57/M57D30
M57D30, also called M57D29, was introduced in 1998.
Applications:
* 184 PS (135 kW; 181 hp)@4000, 390 N·m (290 lb·ft)@1750-3200 models:
E39 530d *Vehicles With Automatic Transmission ONLY*
E46 330d/330xd *Vehicles With Automatic Transmission ONLY*
* 184 PS (135 kW; 181 hp)@4000, 410 N·m (300 lb·ft)@2000-3000 models:
E38 730d *Vehicles With Automatic Transmission ONLY*
E53 X5 3.0d
* 193 PS (142 kW; 190 hp)@4000, 410 N·m (300 lb·ft)@1750-3000 models:
E38 730d
E39 530d
Engine: M57N/M57TU/M57TUD30
M57TUD30 was introduced in 2002. It originally produced 160 kW (215 hp) at 4000 rpm and 500 N·m (370 lb·ft) at 2000-2750 rpm, but was tweaked for 150 kW (201 hp) at 4000 rpm and 410 N·m (300 lb·ft) at 1500-3250 rpm for 2003 and again for 200 kW (268 hp) at 4000 rpm and 560 N·m (410 lb·ft) at 2000-2250 rpm in 2004.
Applications:
* 204 PS (150 kW; 201 hp)@4000, 410 N·m (300 lb·ft)@1500-3250 models:
E46 330d/330Cd/330xd
E83 X3 3.0d
* 218 PS (160 kW; 215 hp)@4000, 500 N·m (370 lb·ft)@2000-2750 models:
E53 X5 3.0d
E60/E61 530d/530xd
E65 730d
* 272 PS (200 kW; 268 hp)@4000, 560 N·m (410 lb·ft)@2000-2250
E60/E61 535d
* 245 PS (180 kW; 242 hp)@4000, 500 N·m (370 lb·ft)@2000-2250
* 286 PS (210 kW; 282 hp)@4000, 580 N·m (430 lb·ft)@2000-2250
Engine: M57TU2D30
M57TU2D30 was introduced in 2007, making its debut in the facelifted E60 and E61.
* M57TU2D30-UL: 197 PS (145 kW; 194 hp)
* M57TU2D30-OL: 235 PS (173 kW; 232 hp)@4000, 500 N·m (370 lb·ft)@2000-2750
* M57TU2D30-TOP: 286 PS (210 kW; 282 hp), 580 N·m (430 lb·ft)
Applications:
* 197 PS (145 kW; 194 hp), 400 N·m (300 lb·ft) models:
E90/E91/E92 325d
E60/E61 525d/525xd
* 231 PS (170 kW; 228 hp)@4000, 500 N·m (370 lb·ft)@2000-2750 models:
E65 730d
E90/E91 325d
E90/E91 330d/330xd
* 235 PS (173 kW; 232 hp) models:
E60/E61, BMW E70, BMW E71
* 286 PS (210 kW; 282 hp), 580 N·m (430 lb·ft) models:
E60/E61 535d
E70 X5 3.0sd
E71 X6 xDrive35d
E83 X3 3.0sd
E90/E91 335d
The above models are listed for information only if you want to to make sure your engine has valves installed, please contact a competent person.
Please note that the information described above is for informational purposes only and does not claim to be reliable. Mr-key.com is not responsible for any repair work you undertake that is related to the topic described in this article.


 (1)_1747998071.jpg)

_1753865226.jpg)
 (1)_1736340291.jpeg)