When it comes to vehicle security, the type of car key you use is crucial. Car keys have evolved dramatically over the years, and today, two main types are commonly available: smart keys and mechanical keys. Each type offers distinct advantages and drawbacks, depending on your preferences, security needs, and budget. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between these two types of keys, their pros and cons, and help you determine which one is best for your vehicle’s security.
Understanding Smart Car Keys
Smart car keys, often referred to as key fobs, have become the standard for most new vehicles. These advanced keys operate using radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, which allows the key to communicate wirelessly with your car. The interaction between the car and the key is based on encrypted signals, enhancing both convenience and security.
Key Features of Smart Car Keys:
- Keyless Entry: One of the most convenient features of smart keys is keyless entry. With this technology, you don’t have to physically insert a key into the lock to open your car. Instead, the key fob transmits a signal to the car’s receiver, unlocking the doors automatically when you approach. This feature is especially useful when your hands are full or during inclement weather.
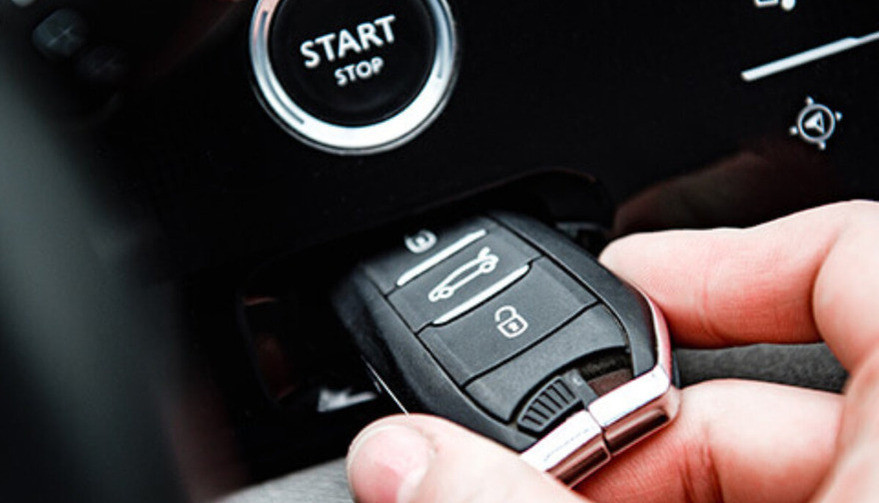
- Push-to-Start Ignition: Many modern vehicles with smart keys feature a push-to-start ignition system. With this technology, you can start your car simply by pressing a button, provided that the key fob is inside the vehicle. No need to insert a key into the ignition, making the process quicker and easier.
- Enhanced Security Features: Smart keys are designed to improve vehicle security. They utilize encrypted signals that are difficult to replicate or hack. Modern key fobs often come with rolling codes, meaning the signal changes each time the key is used, making it nearly impossible for thieves to copy the key’s signal. Additionally, many smart keys are equipped with proximity sensors that automatically lock the doors when the key is a certain distance away, reducing the risk of theft.
- Convenience and Customization: Some smart car keys allow for extra features, such as memory settings for seat adjustments, climate control, and even personalized preferences like music playlists. This adds a layer of comfort and convenience to your driving experience.
Drawbacks of Smart Car Keys:
While smart keys offer numerous benefits, they come with a few challenges:
- Battery Dependence: Smart keys rely on batteries, both within the key fob and sometimes within the car itself. If the battery in your key fob dies, you might find yourself locked out of your vehicle or unable to start it. Fortunately, many vehicles allow you to use a backup mechanical key that is hidden inside the fob itself. However, the reliance on batteries can still be a disadvantage.
- Cost: Replacing a lost or damaged smart key can be expensive, particularly if it involves reprogramming or replacing the vehicle’s security system. Smart keys are generally more costly than mechanical keys, so the price of a replacement key can put a strain on your budget.
- Vulnerability to Hacking: Although modern smart keys are designed to be secure, they are not completely immune to theft. Sophisticated thieves have developed methods of intercepting and cloning key fob signals. While this is still a relatively rare occurrence, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks and take extra precautions to protect your key fob.
- Vulnerability to Water and Extreme Conditions: Smart keys are sensitive to water damage, which makes them less suitable for activities like surfing, open-water swimming, or even heavy rain exposure. Unlike mechanical keys, which are more resistant to environmental factors, electronic key fobs can malfunction if exposed to water or extreme weather conditions. This can leave you stranded or necessitate an expensive replacement.
Understanding Mechanical Car Keys
Mechanical car keys, also known as traditional metal keys, have been in use for over a century. These keys work through a physical mechanism: when inserted into the ignition, they turn to engage the engine. While they are less common in modern vehicles, mechanical keys are still widely used, particularly in older cars or more budget-friendly models.
Key Features of Mechanical Car Keys:
- Simplicity and Reliability: One of the main advantages of mechanical keys is their simplicity. Unlike smart keys, mechanical keys don’t rely on electronics or batteries, making them highly reliable, especially in situations where technology might fail. Whether it’s a long road trip or a cold winter morning, you can always count on your mechanical key to work.
- Affordability: Mechanical keys are far less expensive to produce and replace than electronic keys. If you lose your key, getting a replacement is typically much cheaper. For those on a budget, mechanical keys are a practical option for car security.
- No Risk of Signal Interception: Mechanical keys don’t use radio signals, which means they can’t be intercepted or hacked in the same way smart keys can. There’s no risk of someone remotely copying your key’s signal to gain access to your vehicle.
- Durability: Mechanical keys are often made from durable materials, which means they can last for many years if properly cared for. They don’t require regular battery replacements and are resistant to the kind of wear and tear that might affect electronic systems.
- Suitable for Adventures: Mechanical keys are an excellent choice for outdoor enthusiasts and adventurers. Since they are resistant to water damage, they’re ideal for activities where you might get wet, such as hiking in the rain, kayaking, or camping by a lake. Their durability ensures they’ll keep working even in rugged or wet conditions.
Drawbacks of Mechanical Car Keys:
While mechanical keys have their merits, they also come with limitations:
- Lack of Convenience: Unlike smart keys, mechanical keys require manual operation. You need to physically insert the key into the door and ignition, which may be less convenient, especially when you’re in a hurry or carrying items.
- Security Risks: While mechanical keys can’t be hacked, they are more easily duplicated. If someone gets a hold of your key, they can make a copy, which could put your vehicle at risk. Additionally, older mechanical key systems don’t have the advanced security features found in modern smart keys.
- No Keyless Entry or Push-Start Features: Mechanical keys lack keyless entry and push-to-start ignition, which can make your car less convenient to use. In addition, you won’t have access to any of the advanced features offered by smart keys, such as memory settings or remote start.
When deciding between a smart or mechanical car key, the best choice depends on your individual needs, preferences, and security concerns.
- If you prioritize convenience and advanced security, a smart key might be the right choice for you. Features like keyless entry, push-to-start ignition, and superior encryption provide a higher level of comfort and safety. If you have a newer vehicle or enjoy the latest technology, a smart key will enhance your driving experience.
- If you value simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness, a mechanical key may be the better option. It’s a great choice for older vehicles, drivers on a budget, or those who don’t need the added complexity of modern electronic systems. Mechanical keys are also ideal for people who want a straightforward, low-maintenance solution to car access.
Regardless of which type of key you choose, it’s important to maintain backups and ensure that your keys are properly cared for. If you opt for a smart key, remember to replace the batteries regularly and store the key in a safe place to prevent loss or theft. If you use a mechanical key, consider having a spare made to avoid being locked out of your vehicle in case of misplacement.
For ultimate peace of mind, having both types of keys can be a smart investment—offering the convenience of advanced features alongside the reliability of a traditional backup. Together, they ensure you’re prepared for any situation while adding an extra layer of security.


_1751630541.jpg)
_1733224387.jpg)
_1736340211.jpg)